|
|
home |
|
By 2030, the number of older Americans
is expected to double from 35 million to 70 million. The percentage of the
total population that is aged 65 or older is expected to grow from 12 percent in
2000 to 20 percent in 2030. The growing number of older adults will place
increasing demands on the public health system and on medical and social
services. Lack of physical activity and poor diet are the major causes of
an epidemic of obesity that is affecting the elderly as well as middle-aged and
younger populations. An estimated 18 percent of adults over age 65 in the
United States are obese, and another 40 percent are overweight, putting them at
substantially increased risk for diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease,
along with other chronic diseases. In 2000, the total costs of overweight and
obesity combined was estimated to be $117 billion.
Percentage of Obese, Overweight, and
Healthy Weight Adults > Age 65, 2000
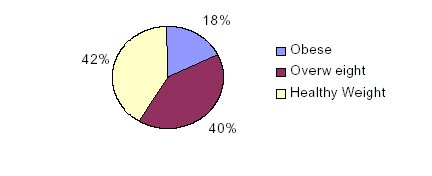
Source:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease
Prevention and Health Promotion. Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.
Trend Data, Nationwide. April 1, 2002.
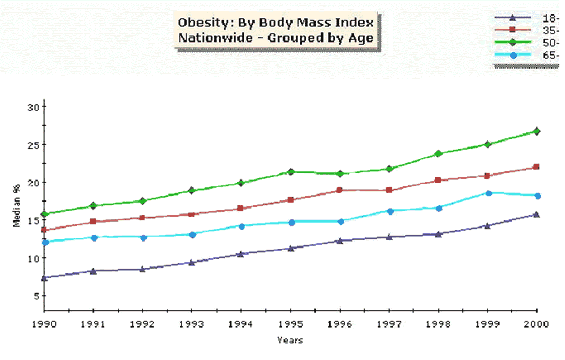
This represents a substantial increase over the
past decade. Since 1990, the prevalence of obesity has increased more than 50
percent in the elderly, and even more in some younger age groups
Graph of Body Mass Index
Source:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease
Prevention and Health Promotion. Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.
Trend Data, Nationwide. April 1, 2002.
Currently, almost one-third of total U.S. health
care expenditures is for older adults (over age 65). Health care
expenditures for people aged 65 years or older are four times that for
40-year-olds. By 2030, health care spending will increase by 25 percent,
simply because the population will be older, before inflation or new
technologies are taken into account. Estimates from a study by Harvard
researchers calculated that the direct medical costs attributable to inactivity
and obesity accounted for nearly 10 percent of all health care expenditures in
the United States. Being inactive results in loss of muscle strength and
balance and increases the risk of falls. Every year, fall-related injuries
among older people cost the nation more than $20.2 billion. By 2020, the
total annual cost of these injuries is expected to reach $32.4 billion.
The impact of a lack of physical activity on
medical care costs is likely to grow as a result of an aging population, unless
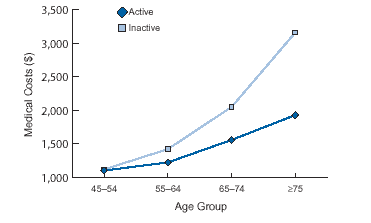
trends in physical activity change. One study (CDC) has shown that the
direct medical costs of inactive adults are substantially higher than those of
active adults. These excess costs increase with age and is especially
notable in women. The data imply that society may be able to reap larger
benefits in terms of lower health care costs by improving physical activity
levels in older adults, as compared with any other age group.
Annual Medical Costs of Active and
Inactive Women (Aged 45 or Older) Without Physical Limitations
Source:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Promoting Active Lifestyles
Among Older Adults. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and
Health Promotion. Nutrition and Physical Activity. |